太阳风的形成机制: 起源、加速、加热
自从1962年水手2 号飞船证实高速太阳风的存在以来,太阳风的形成机制一直是国际前沿课题。研究太阳风的形成对认识恒星物质、能量输出等基本自然现象以及粒子加速和磁重联等基本物理过程是至关重要。太阳风又是联系日地的媒质,太阳爆发通过太阳风传到地球空间,产生空间天气突变事件,从而影响人类的空间环境。
该方向取得的亮点研究成果有:(1)发现太阳风起伏中存在波动和湍流的二重性,(2)发现太阳风加热的能源来自湍流串级能量,创建了描述太阳风湍流传输特性的“类WKB湍流理论”,(3)创建了太阳风阿尔芬湍流串级加热理论和推广的湍流间歇理论;(4)发现太阳风流动起源于磁漏斗结构中的过渡区,提出太阳风初始外流是由光球超米粒组织对流运动驱动的新观点,并建立相应数值理论模型;(5)发现太阳风动力学湍流的二元波动性,并提出其耗散加热途径;(6)发现太阳风初始外流是间歇高速的;(7)发现阿尔芬波在太阳风源区被磁重联激发、传播和耗散,是太阳风形成的重要能量来源。到目前共发表SCI论文百余篇,包括2005年在《科学》(Science)上发表的以北京大学为第一研究单位、涂传诒院士为第一作者的研究论文(Research Article),编著出版了2本学术书籍。发表的研究论文被SCI引用3000多次。
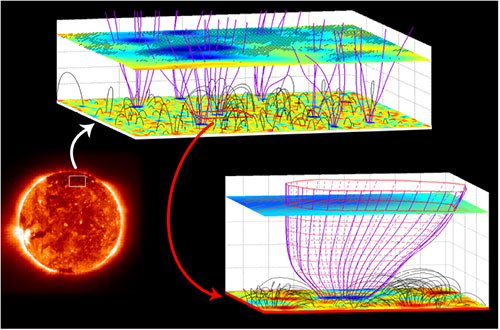
图-1. Genesis of solar wind in coronal funnel.
相关论文:
1.Tu C.-Y., The damping of interplanetary Alfvenic fluctuations and the heating of the solar wind, J. Geophys Res., vol.93, No.A1, p.7-20,1988
2.Tu, C. Y. and E. Marsch, A model of solar wind fluctuations with two components: Alfven waves and convective structures, J. Geophys. Res., 98, 1257—1276, 1993
3.Tu, C.Y., Structures, Waves, and Turbulence in Solar Wind, Space Sci. Rev., 73, 1—210, 1995
4.Tu, C.Y. and E. Marsch, Two-fluid model for heating of the solar corona and acceleration of the solar wind by high-frequency Alfven waves, Solar Phys., 171, 363—391, 1997
5.Tu, C.Y. and E. Marsch, On cyclotron wave heating and acceleration of solar wind ions in the outer corona, J. Geophys. Res., 106(A5), 8233—8252, 2001
6.Tu, C.-Y, C. Zhou, E. Marsch, L.D. Xia, L. Zhao et al, Solar wind origin in coronal funnels, Science, 308, 519-523, 2005
7.He, J.-S., Marsch, E., Tu, C.-Y., Tian, H., Excitation of Kink Waves Due to Small-Scale Magnetic Reconnection in the Chromosphere? ApJL, 705, 217-222, 2009.
8.He J-S, Marsch E, Tu C-Y, Yao S, Tian H. Possible Evidence of Alfvén-cyclotron Waves in the Angle Distribution of Magnetic Helicity of Solar Wind Turbulence. ApJ, 2011, 731, 85H, doi:10.1088/0004-637X/731/2/85.
9. Tian, H., DeLuca, E. E., Cranmer, S. R., et al., Prevalence of small-scale jets from the networks of the solar transition region and chromosphere, Science, 346, 1255711, 2014